08:01 AM | 31 Dec 2024 | By Admin
Understanding Syndromes: What They Are and How They Impact Health
When we hear the word “syndrome,” it’s often associated with a specific set of symptoms or conditions that occur together. Syndromes are complex, and they can affect individuals in different ways. While some syndromes are well-known, such as Down syndrome or chronic fatigue syndrome, many are less familiar but still significant in understanding how health conditions manifest. In this blog, we’ll explore what syndromes are, how they’re diagnosed, and how they impact overall health.
What Is a Syndrome?
A syndrome is a collection of signs, symptoms, or characteristics that regularly occur together. Unlike a disease, which is a specific condition with a known cause (such as a bacterial infection), a syndrome does not always have a clear, identifiable cause. Instead, it refers to a group of symptoms that happen together in a way that suggests a particular health issue.
Syndromes can range from rare and poorly understood conditions to common, well-documented conditions that are widely recognized in the medical community. For example, Down syndrome is a genetic condition characterized by intellectual disability and physical characteristics such as a flat facial profile and almond-shaped eyes. Chronic fatigue syndrome, on the other hand, is a complex disorder defined by extreme fatigue that does not improve with rest and often worsens with physical or mental activity.
Common Types of Syndromes
There are countless syndromes that affect individuals across the globe, and many of them are related to a variety of factors such as genetics, infections, environmental factors, or lifestyle choices. Here are a few examples:
1. Down Syndrome
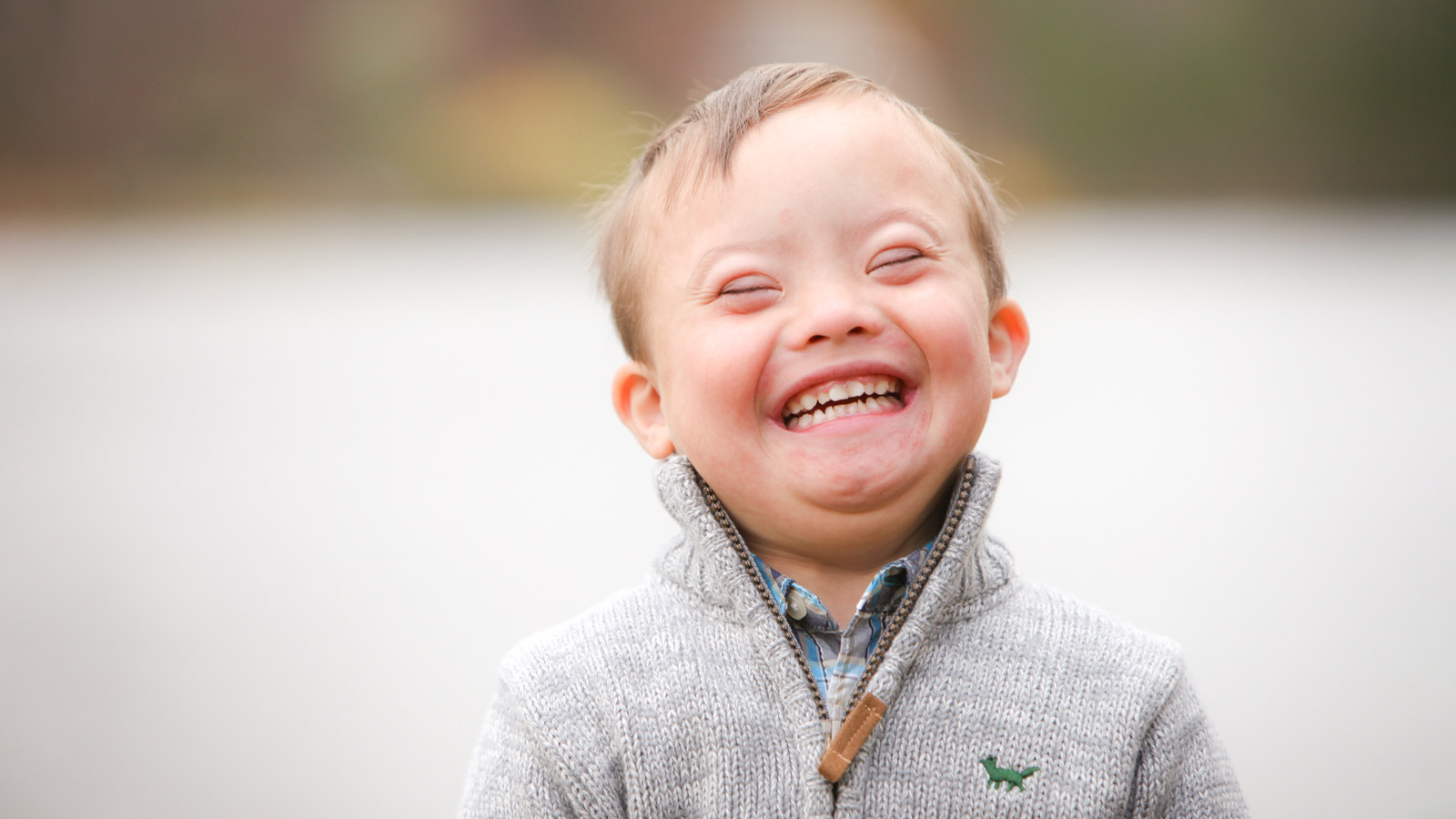
Down syndrome is one of the most well-known genetic syndromes, occurring when a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21. This extra chromosome causes developmental and physical differences, including intellectual disabilities, characteristic facial features, and other health issues like heart defects or vision problems. People with Down syndrome can live fulfilling lives with appropriate care, support, and early interventions.
2. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
Chronic fatigue syndrome, also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME), is characterized by severe, persistent fatigue that doesn't improve with rest. This syndrome can be disabling and affects the person’s ability to function in daily life. The exact cause of CFS is unknown, but it is believed that infections, immune system issues, or extreme stress may play a role. Common symptoms include muscle pain, memory problems, and unrefreshing sleep.
3. Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects females, resulting from the partial or complete absence of one of the X chromosomes. This condition leads to growth issues, infertility, and sometimes heart or kidney problems. People with Turner syndrome may also experience learning difficulties, particularly in spatial reasoning and mathematics, but their intelligence is typically within the average range.
4. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation. The exact cause of IBS is unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines, stress, and sensitivity to certain foods. IBS can be managed through diet changes, stress management, and medications.
5. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that results from pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand or fingers. It is often caused by repetitive movements, such as typing or using a computer mouse. Treatment typically involves rest, ergonomic adjustments, wrist braces, or, in severe cases, surgery.
How Are Syndromes Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a syndrome often requires a detailed evaluation of symptoms and medical history. Because many syndromes have overlapping symptoms with other conditions, it can sometimes be challenging to pinpoint the exact cause. A doctor may:
- Conduct physical exams: A healthcare provider will often assess the individual’s physical condition and check for signs or symptoms associated with the syndrome.
- Review medical history: Understanding the patient’s personal and family medical history can help identify patterns or inherited conditions.
- Order laboratory tests: Blood tests, genetic tests, or imaging studies may be used to rule out other conditions or confirm the diagnosis.
- Monitor symptoms over time: For some syndromes, tracking symptoms over time is essential to understand the condition and how it evolves.
Impact of Syndromes on Health
Syndromes can have a wide range of effects on health, depending on the condition. For some, symptoms may be mild and manageable, while others can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life.
Some common impacts include:
- Physical health: Many syndromes involve physical symptoms such as pain, fatigue, or limitations in movement. Some syndromes, like Turner syndrome or Down syndrome, may also be associated with congenital health issues like heart defects or hormonal imbalances.
- Mental and emotional health: Living with a syndrome can take an emotional toll, especially if the condition leads to social isolation, chronic pain, or difficulty performing everyday tasks. People with chronic conditions may experience anxiety, depression, or frustration.
- Social impacts: People with visible or well-known syndromes may face social stigma, which can affect their relationships, education, or employment opportunities. Early diagnosis and support are key to improving long-term outcomes and reducing negative social effects.
- Cognitive and developmental issues: Some syndromes, like Down syndrome, may involve developmental delays or intellectual disabilities. Early intervention through therapies and educational support can make a significant difference in cognitive development and overall success in life.
Treatment and Management of Syndromes
The treatment for a syndrome depends on the specific condition and its severity. While some syndromes can be managed with medications, therapies, or lifestyle changes, others may require lifelong care and support.
1. Medications
Some syndromes may require medications to manage symptoms or underlying conditions. For example, people with chronic fatigue syndrome may take medication to relieve pain or manage sleep disturbances, while individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome might use anti-inflammatory drugs or steroids to reduce swelling.
2. Therapy and Rehabilitation
Therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy can help individuals manage the symptoms of certain syndromes, especially if there are developmental or motor impairments.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
For some syndromes, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. For example, people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may find relief by adjusting their diet and managing stress, while those with chronic fatigue syndrome might need to rest more frequently and pace their activities.
4. Support Systems
Building a strong support system is crucial. Whether it’s through family, friends, or support groups, having a network of people who understand the challenges of living with a syndrome can help improve emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Syndromes encompass a broad range of health conditions, each with its own set of challenges and treatment options. Understanding the symptoms and causes of syndromes is the first step toward finding effective management strategies. With early diagnosis, support, and the right treatment, individuals living with syndromes can lead fulfilling lives. If you or someone you know is dealing with a syndrome, reaching out to a healthcare provider for support and guidance is crucial in managing symptoms and improving overall health.